The genus of humans is known as 'Homo.'
Homo is a member of the family of 'great apes.' Modern human beings, also known
as Homo sapiens, are closely related to the great apes' primate group of
species, including the chimpanzee and the gorillas. Genetic analysis suggests
that these primates had the latest common ancestors (LCA) 9 to 6 million years ago. Evidence shows that humans share about
98.7 percent of their DNA with chimpanzees. Therefore, a chimpanzee is
considered a more recent common ancestor than a gorilla. Several Homo species
have been discovered that contributed to the evolution of modern Homo sapiens.
A timeline for the evolution of humans on Earth is shown in Figure 2.10. Several Homo species that evolved over time were distinct compared to other animals. For example, one of the distinguishable
features of humans is the ability to walk on two legs. It is a unique trait
named bipedalism. Early fossils and archeological remains indicate that
bipedalism evolved about 6 to 4 million years ago (mya). Furthermore, several
fossils belonging to the period from 6 mya to 2 mya have been found only in
Africa; therefore, it is assumed that human evolution started in Africa.
Several other members of the genus Homo,
such as Homo habilis and Homo erectus, are known to have evolved. It is
estimated that they have survived for about 2 million years. Neanderthals, another member of the genus Homo, evolved in Europe and West
Asia about 400,000 years ago. A comprehensive dating of the Neanderthal bones
and tools from hundreds of European sites indicates that European Neanderthals
died out between 41,000 and 39,000 years ago. However, the Neanderthals
contributed to the DNA of modern humans between 60,000 and 50,000 years ago
through interbreeding. In 2010, scientists discovered fossilized
bones belonging to a human species named Homo Denisova found in Denisovan caves
in Siberia. Furthermore, recent DNA mapping studies have found that the human
population of Europe and the Middle East has between one to four percent of the unique human DNA of the Neanderthal DNA. Also,
in Australia, Melanesians and Aboriginal Australians have 6% of the unique
human DNA of the Denisovan DNA. Therefore, we conclude that modern human beings
have evolved mainly from the Homo sapiens and, to a small extent, from the
Neanderthals and the Denisovans. Early humans started migrating out of the
southern part of Africa. They migrated to other continents in one or perhaps
two major migration waves. The first migration happened in Asia about 2 million
years ago. Migration to Europe occurred between 1.5 million to 1 million years
ago. The spreading of modern humans into other parts of the world happened much
later. Modern humans migrated to Siberia and Australia about 60000 to 35000
years ago. They arrived in America between 30000 to 15000 years ago.
Archeological data based on carbon dating, linguistic study, and genetic data
based on the molecular clock are used to estimate the spread of humans in
various regions worldwide. The studies indicate that it is the Homo sapiens who
have displaced all other human species and survived. We have presented the timeline for the
beginning of life. It took more than 9 billion years since the beginning of the
universe for the Sun and Earth to be born. It is shown that the early signs of
life are more than 4 billion years old, as determined from the analysis of the
fossils that lay preserved in the rocks. The techniques for the fossil analysis
using radiocarbon dating can be relied upon, providing results with known
accuracy. These techniques suggest that all life forms evolved from a common
ancestor as the genes comprising the last universal common ancestor are
identified. The well-known theory of evolution spelled the emergence of species
of higher intelligence from simpler life entities. Early signs of humans that
appeared in the last few million years evolved into several Homo species,
although Homo sapiens one is the only surviving today. Dawn of Humans
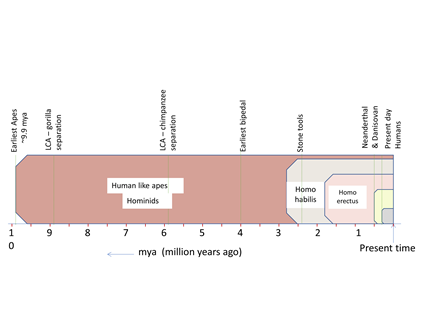
Figure 2.10: Graphics illustrating the timeline for human
evolution on Earth.